Developer Guide
Table of Contents
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
- Appendix: Effort
Acknowledgements
- This project is created based on the AddressBook-Level3 project by the SE-EDU initiative.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
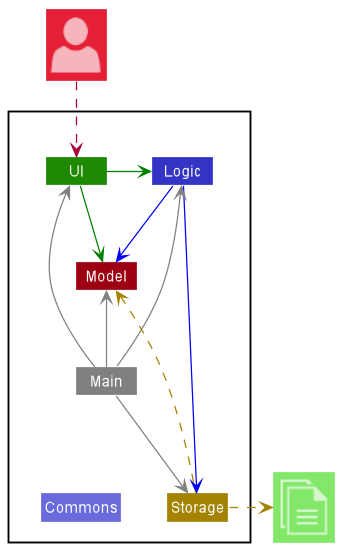
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the Tinner. Tinner follows a multi-layered architecture where the lower layers are independent of higher layers. For example, Main can use methods found in Storage but not the other way around.
Below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Each of the four components,
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - exposes its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which implements the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component (see the class diagram given below) defines its API in the Logic.java interface and exposes its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which implements the Logic interface.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command deleteCompany 1 when in project view.

The sections below give more details of each component.
UI Component
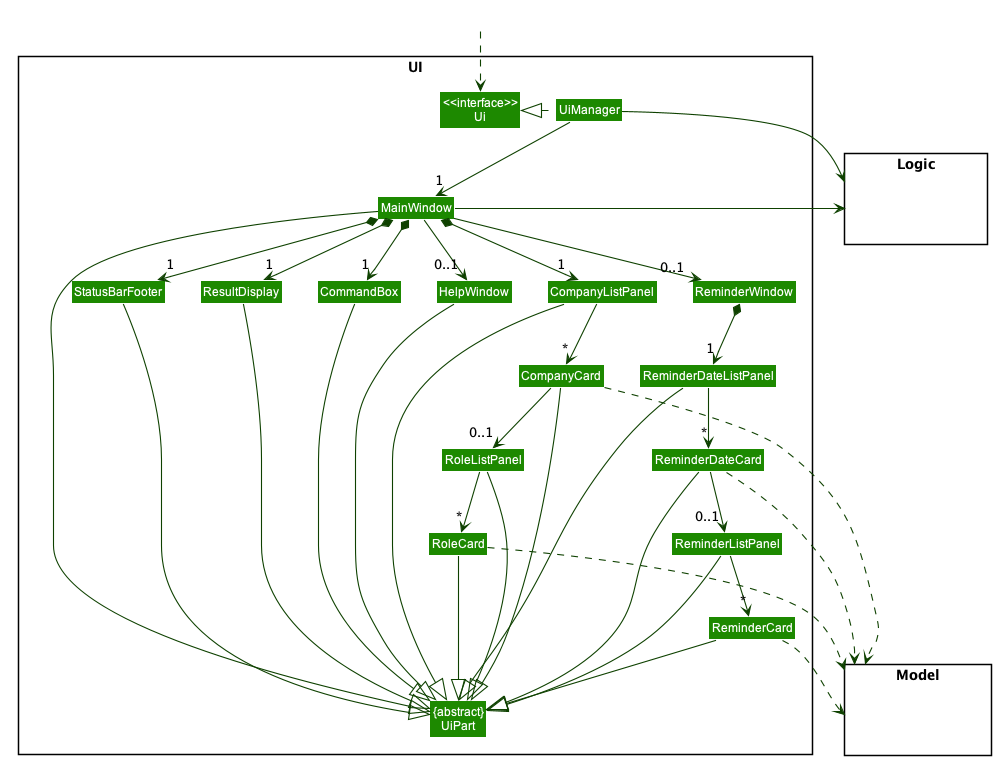
API :
Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, CompanyListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The CommandBox and ResultDisplay appear at the top of the application for the user
to interact with the application.
The CompanyListPanel appears at the center of the application displaying key information of Company
from CompanyCard.
The RoleListPanel appears at the bottom of CompanyCard displaying key information of Role from RoleCard.
The ReminderWindow appears as a separate window displaying key information of Reminder from ReminderCard.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that theUIcan be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysCompanyandRoleobjects residing in theModel.
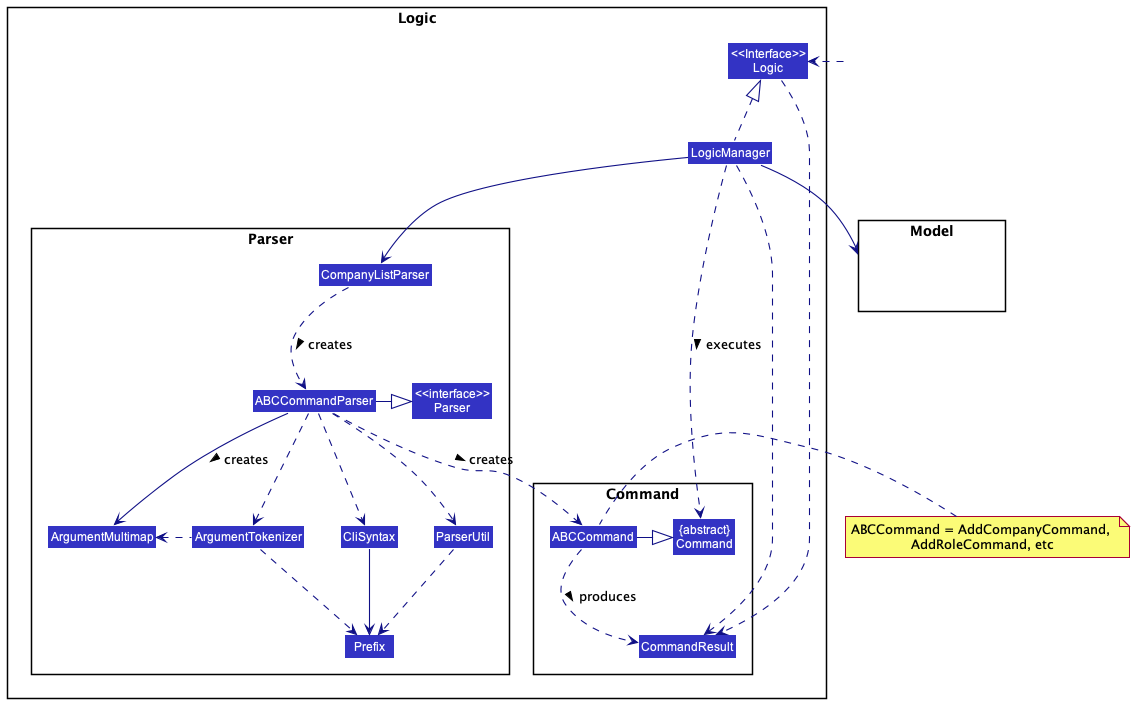
Logic Component
API :
Logic.java

How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it uses theCompanyListParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject (or more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,AddCompanyCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to add a company). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
The Sequence Diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for the execute("deleteCompany 1") API call.
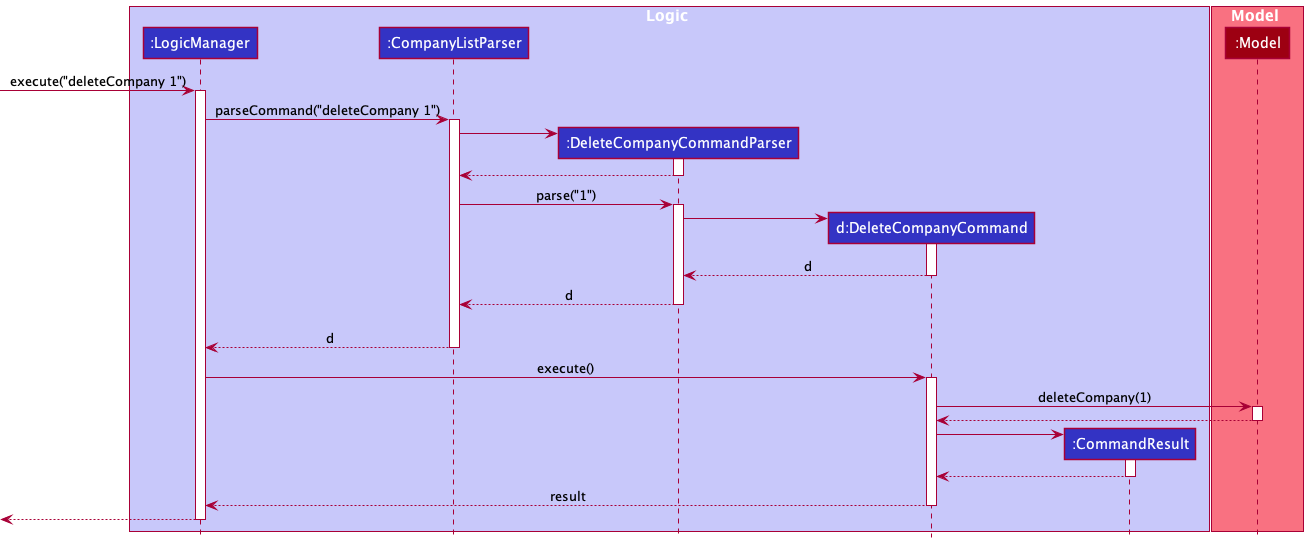
DeleteCompanyCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
The other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command can be represented as follows:
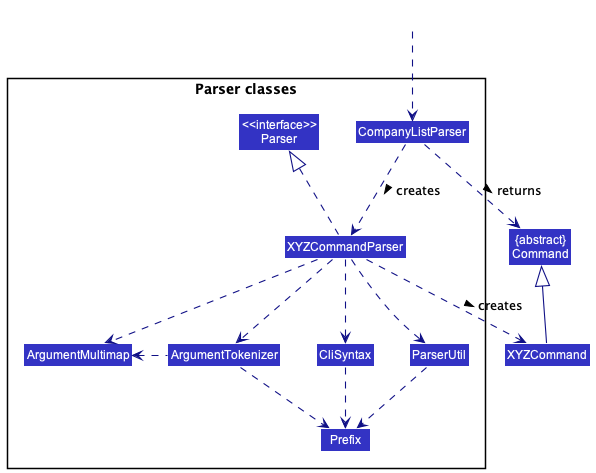
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
CompanyListParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCompanyCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above (e.g.ArgumentMultimap,ParserUtil, etc.) to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCompanyCommand) which theCompanyListParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCompanyCommandParser,DeleteCompanyCommandParser, …) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
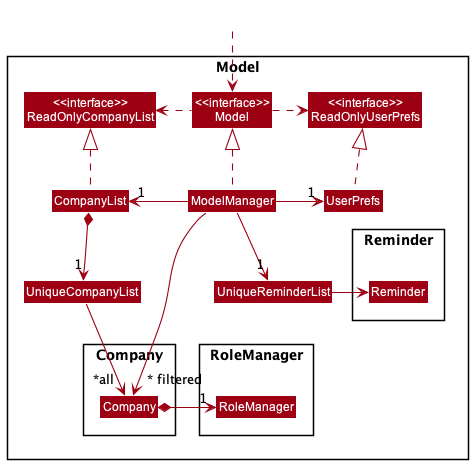
Model Component
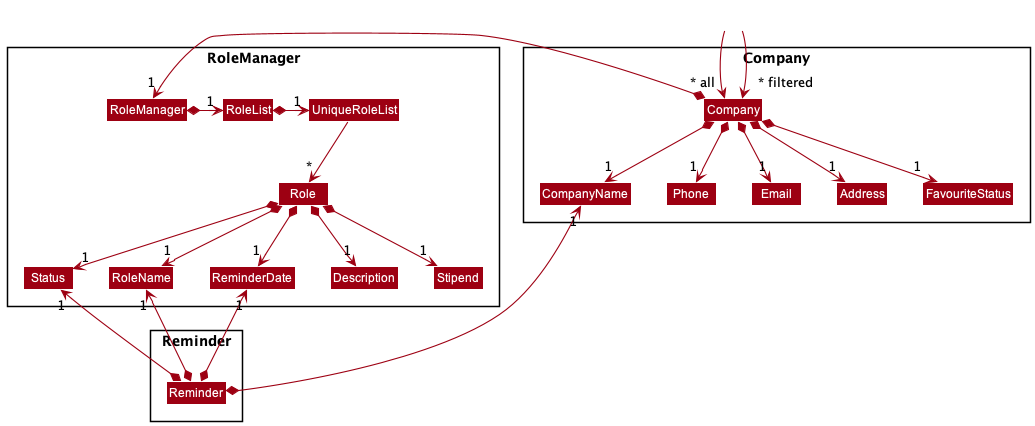
Breakdown of the Company, RoleManager and Reminder packages:
API :
Model.java
The Model component,
- stores the company list data i.e., all
Companyobjects (which are contained in aUniqueCompanyListobject). - stores the currently selected
Company,RoleandReminderobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableListthat can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - the
Reminderobjects store data of a role in a company that has a reminder date which is within the reminder window. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
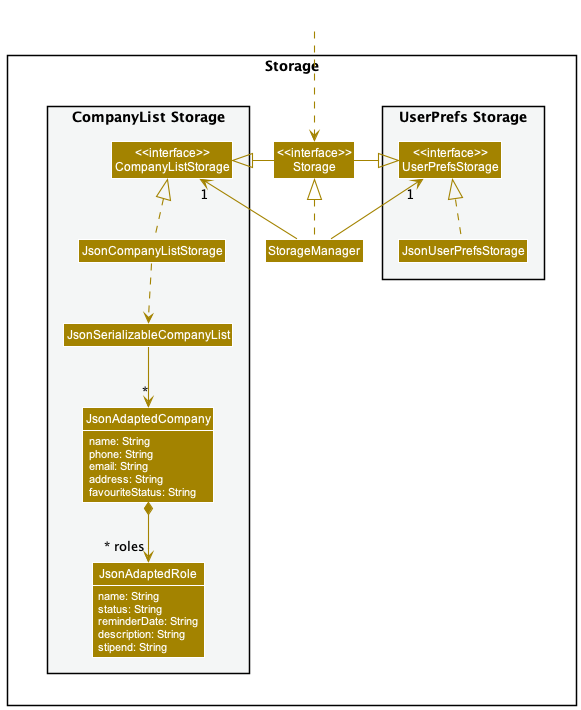
Storage Component
API :
Storage.java
The Storage component,
- can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. - can save
JsonAdaptedCompanyobjects inJsonSerializableCompanyListin json format and read it back. - can save
JsonAdaptedRoleobjects inJsonAdaptedCompanyin json format and read it back - inherits from both
CompanyListStorageandUserPrefStorage,meaning that it can be treated as either one (if the functionality of only one is required) - depends on classes like
CompanyandRolein theModelcomponent (as it is theStoragecomponent’s job to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
The JsonAdaptedCompany also contains a list of roles in List<JsonAdaptedRole> format, as show in the class diagram above.
Implementation
Due to some of our features having duality in its implementaion, we have decided to omit those features exclusive
to company that have a role counterpart. This is due to the role counterpart being more complicated as it builds
directly on top of the features exclusive to company.
Add role feature
The addRole command for the Role item allows the user to add a new role by specifying
the company index this role is attached to, and the details of the role with the appropriate prefix.
The fields of the Role that are necessary are as follows:
RoleNameStatus
The fields of the Role that are optional are as follows:
ReminderDateDescriptionStipend
Implementation
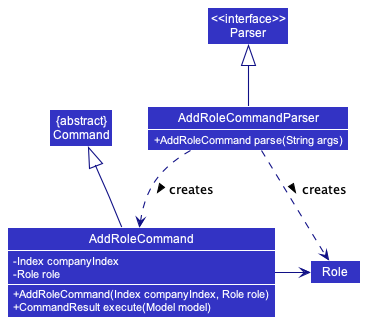
The addRole command is primarily implemented by AddRoleCommandParser a class that extends Parser,
and AddRoleCommand, which is a class that extends Command.
The AddRoleCommandParser has three main objective
- Ensure user inputs all necessary fields.
- Ensure validity of all fields from user input.
- If 1 and 2 are satisfied, store the user inputs into a new
Roleobject.
If all three objectives are achieved, the newly created Role object would then be passed to AddRoleCommand
Upon completion of executing addRole command, the displayed list of roles would be dynamically updated accordingly.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the add role feature behaves at each step:
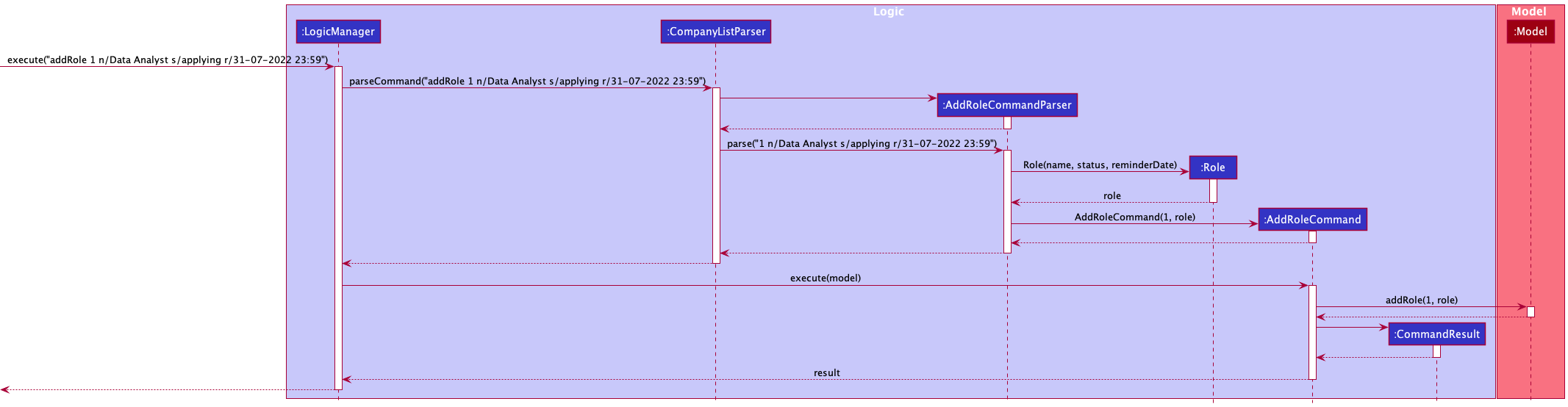
- The user executes the command
addRole 1 n/Data Analyst s/applying r/31-07-2022 23:59to add a new role into the 1st company. - Then the
AddRoleCommandParser#parse()parses and creates aRoleobject with fields to be added such as the roleNameData Analystbefore creating an instance ofAddRoleCommandwith it. - The
AddRoleCommandParserreturns theAddRoleCommandto theLogicManager.LogicManagerinvokesAddRoleCommand#execute()which validates if role is present according to the company and role indexes, if so add the new role into the company’sRoleManager. - The
LogicManagerthen returns theCommandResulttoMainWindowin order to display changes to the user.
The following sequence diagram shows how the addRole command operation works with the
valid user input addRole 1 n/Data Analyst s/applying r/31-07-2022 23:59:
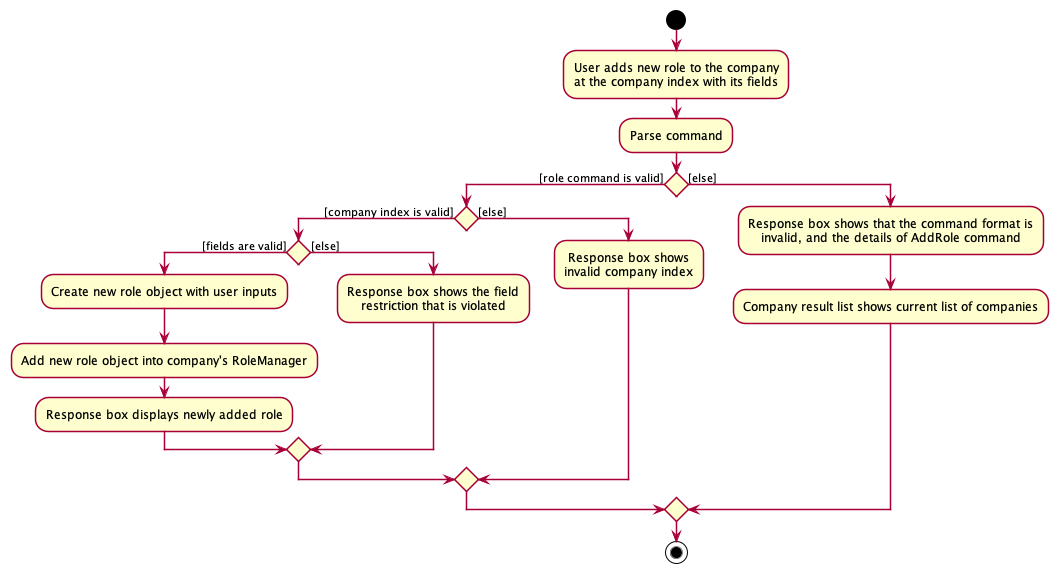
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes an addRole command:
Design considerations
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Abstract
Role’s storage to be handled byRoleManager- Pros:
- Reduce coupling between
RoleandCompanyas theaddRolefeature is implemented via theRole’s model instead of theCompany’s model. -
Companydoes not need to worry about the implementation details ofRole, which it shouldn’t in the first place.
- Reduce coupling between
- Cons:
- Increases code duplication as
Companyclass has to retain methods which acts as signals for invoking execution of methods inRole.
- Increases code duplication as
- Pros:
- Alternative 2 (used in v1.2):
Roleis stored in a Java List as an attribute ofCompanyclass- Pros:
- All commands related to
Rolecan be implemented and handled onCompanylevel, reduces code repetition. -
AddRolefeature could be achieved via calling on an attribute ofCompany.
- All commands related to
- Cons:
- Exposes the internal implementation of
RoletoCompanyeven though they are different. - Increases coupling between
RoleandCompany.
- Exposes the internal implementation of
- Pros:
Edit role feature
The editRole command for the Role item allows the user to update any fields by specifying
the company index, role index and prefixes of the fields to be updated.
The aforementioned fields of the Role that can be modified are as follows:
RoleNameStatusReminderDateDescriptionStipend
Implementation
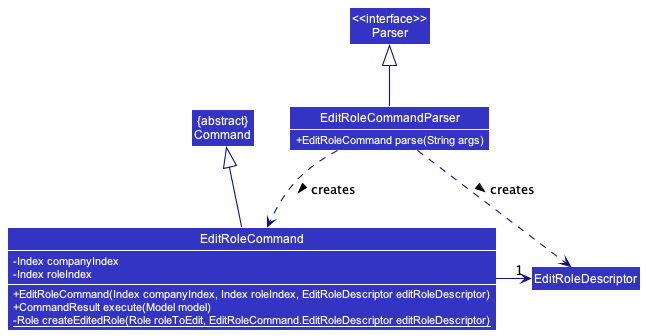
The editRole command is primarily implemented by EditRoleCommandParser a class that
extends Parser, and EditRoleCommand, which is a class that extends Command. The EditRoleCommand has
an inner class EditRoleDescriptor that holds the changes to fields of the Role to be modified.
Upon completion of executing editRole command, the displayed list of roles would be dynamically updated accordingly.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the edit role feature behaves at each step:
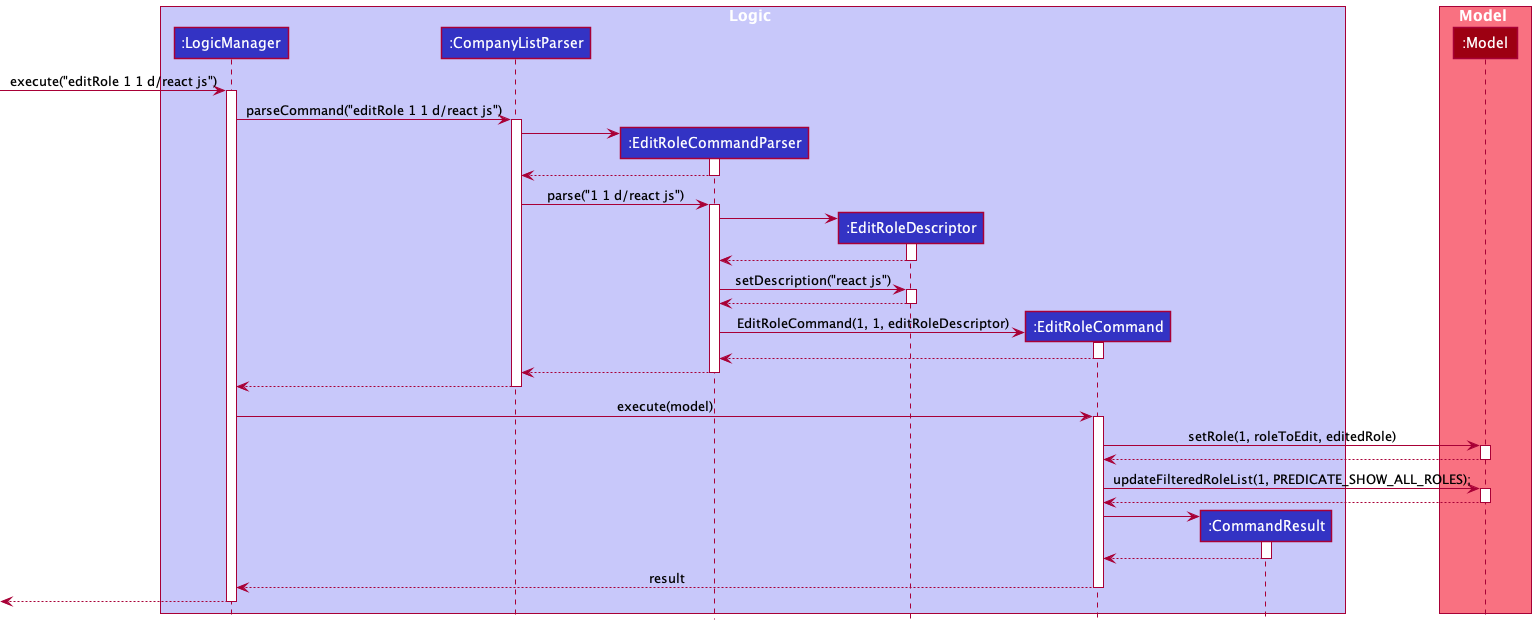
- The user executes the command
editRole 1 1 d/react jsto edit the description in the 1st role from the 1st company. - Then the
EditRoleCommandParser#parse()parses and creates anEditRoleDescriptorobject with fields to be modified such as the descriptionreact jsbefore creating an instance ofEditRoleCommandwith it. - The
EditRoleCommandParserreturns theEditRoleCommandtoLogicManager.LogicManagerinvokesEditRoleCommand#execute()which validates the company and role indexes, if so edit its description to the user input. - The
LogicManagerthen returns theCommandResulttoMainWindowin order to display changes to the user.
The following sequence diagram shows how the editRole command operation works with the valid user input editRole 1 1 d/react js:
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes an editRole command:
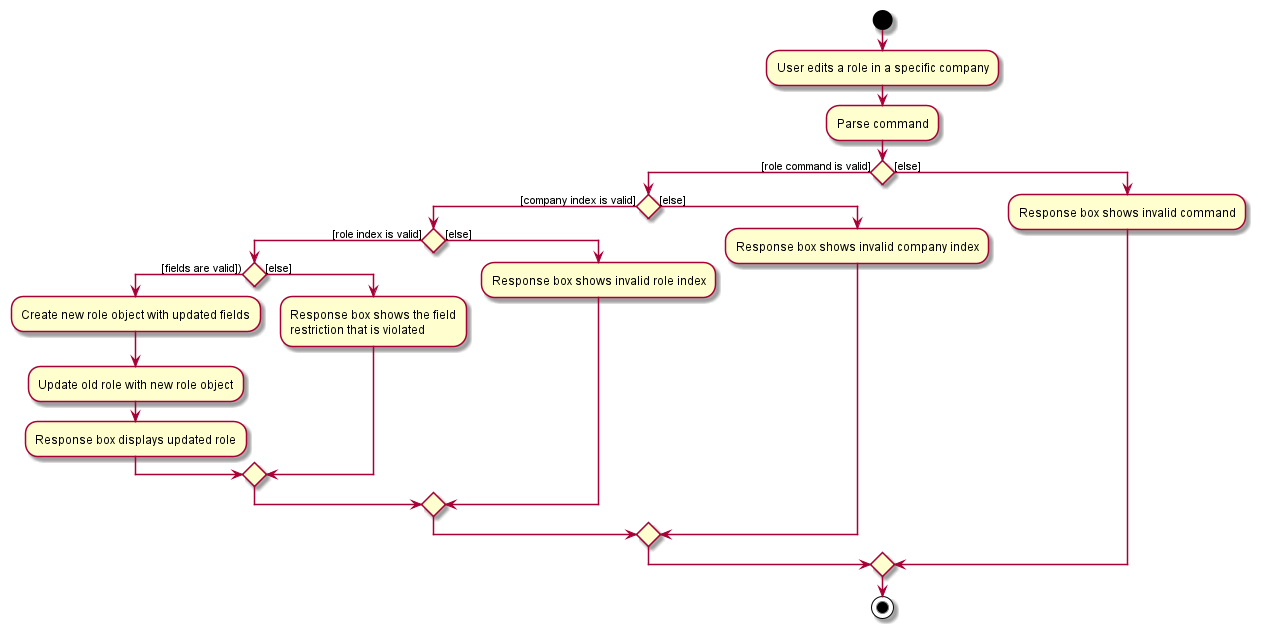
Design considerations
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Logic components interact with the
Modelinterface solely and not directly with model’s internal components:Company,RoleManager,UniqueRoleList.- Pros:
- The
Modelinterface acts as a Façade to allow clients such asLogicto access to the functionalities of its internal components without exposing the implementation details. Thus, reducing coupling betweenModeland other components as all functionalities of modifyingRolecan be accessed via theModelinterface. - This increases maintainability as
EditRoleCommandwill only interact withModelinterface with little concern to any changes in the implementation details of the internal components ofModel.
- The
- Cons:
- This requires additional code within
Modelas more methods are needed for other components to access the functionality of its internal components.
- This requires additional code within
- Pros:
- Alternative 2 (used in v1.2):
Modelallows clients to access its internal components directly such asCompany,RoleManager,UniqueRoleListto modifyRole.- Pros:
- No additional code is needed as clients can operate directly on the internals of
Model.
- No additional code is needed as clients can operate directly on the internals of
- Cons:
- This exposes the internal implementation of
Modeland increases coupling betweenEditRoleCommandand,Company,RoleManagerandUniqueRoleList. - It is harder to maintain as any changes to the internal implementation of
Modelwill affect the implementation ofEditRoleCommand.
- This exposes the internal implementation of
- Pros:
Delete role feature
The deleteRole command for the Role item allows the user to delete any role under a Company item by specifying the company index and role index that which are associated with the Role item to be deleted.
Implementation
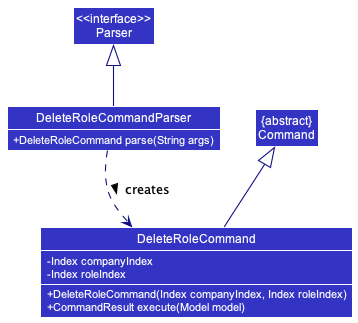
The deleteRole command relies on the DeleteRoleCommandParser, a class that extends Parser, as well as DeleteRoleCommand, which is a class that extends Command.
The DeleteRoleCommand, upon completion, dynamically updates the displayed list of roles accordingly.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the delete role feature behaves at each step:
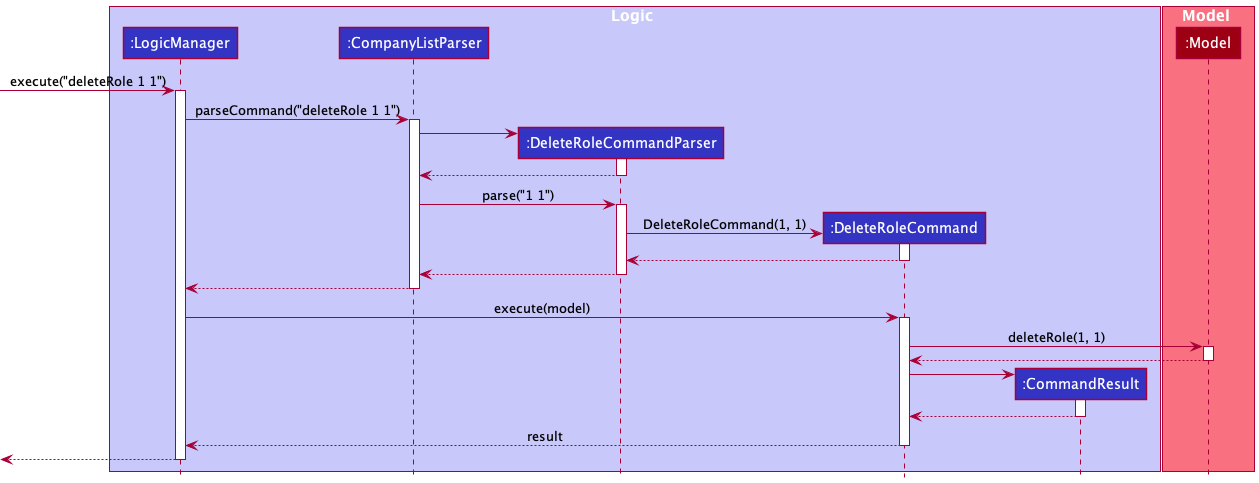
- The user executes the command
deleteRole 1 1to delete the 1st role from the 1st company. - Then the
DeleteRoleCommandParser#parse()parses and creates an instance ofDeleteRoleCommandwith the company index and role index parsed. - The
DeleteRoleCommandParserreturns theDeleteRoleCommandtoLogicManager.LogicManagerinvokesDeleteRoleCommand#execute()which validates if role is present according to the company and role indexes, if so deletes the role. - The
LogicManagerthen returns theCommandResulttoMainWindowin order to display the changes to the user.
The following sequence diagram shows how the deleteRole command operation works with the user input deleteRole 1 1:
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes an deleteRole command:
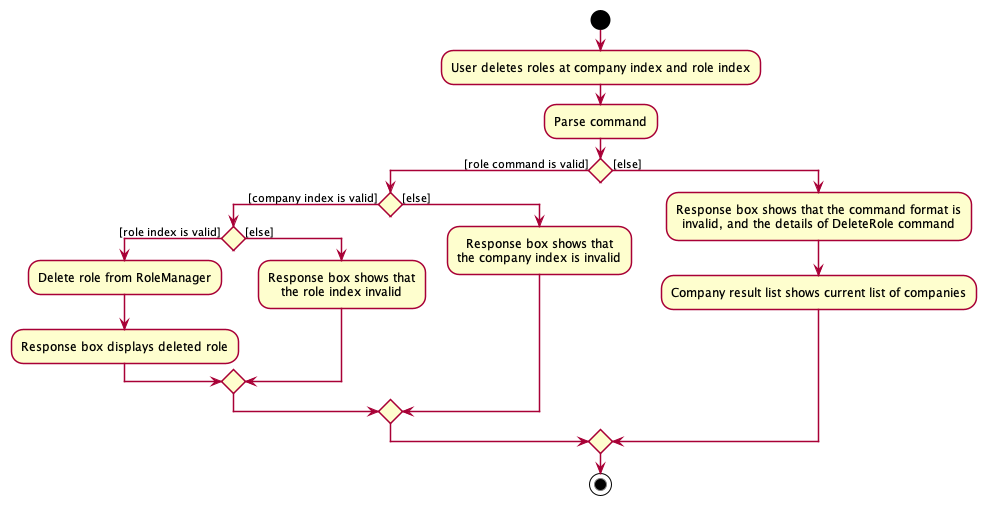
Design considerations
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Split
deletefeature intodeleteCompanyanddeleteRole- Pros:
- Prevents users from accidentally deleting an entire company when intended action was to only delete roles.
- More intuitive to users as it is easier to associate the differences with words compared to format of command.
- Cons:
- Increases code repetition due to both delete features have similar components.
- Pros:
- Alternative 2 (used in v1.2): Have a unified
deletefeature that changes functionality based off user input.- Pros:
- Reduce code repetition due to not having two different class and two different parsers.
- Cons:
- User might accidentally delete an entire
companyif command was sent too early, resulting in thecompanyand all associatedrolesbeing deleted. - Due to the lack of an undo feature, this is can be a massive problem.
- User might accidentally delete an entire
- Pros:
Find feature
The find feature allows users to filter the company list to find roles by specifying company name keywords and role name keywords.
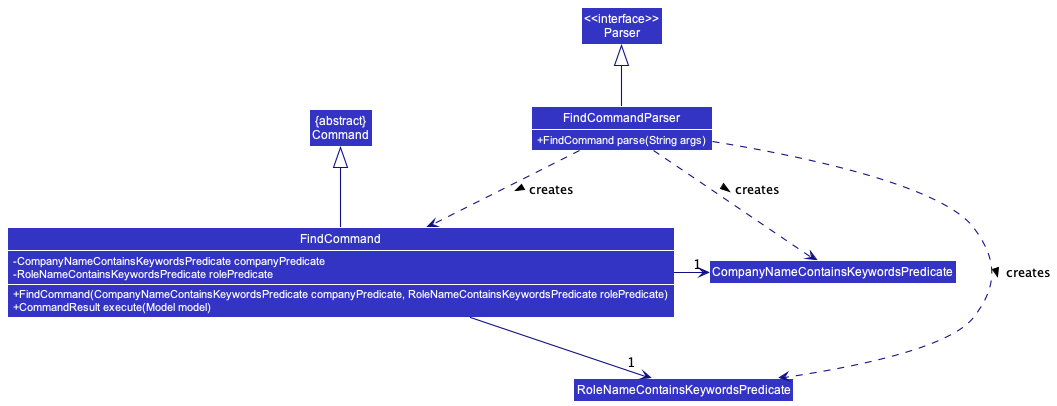
Implementation
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the find feature behaves at each step:
- The user executes the command
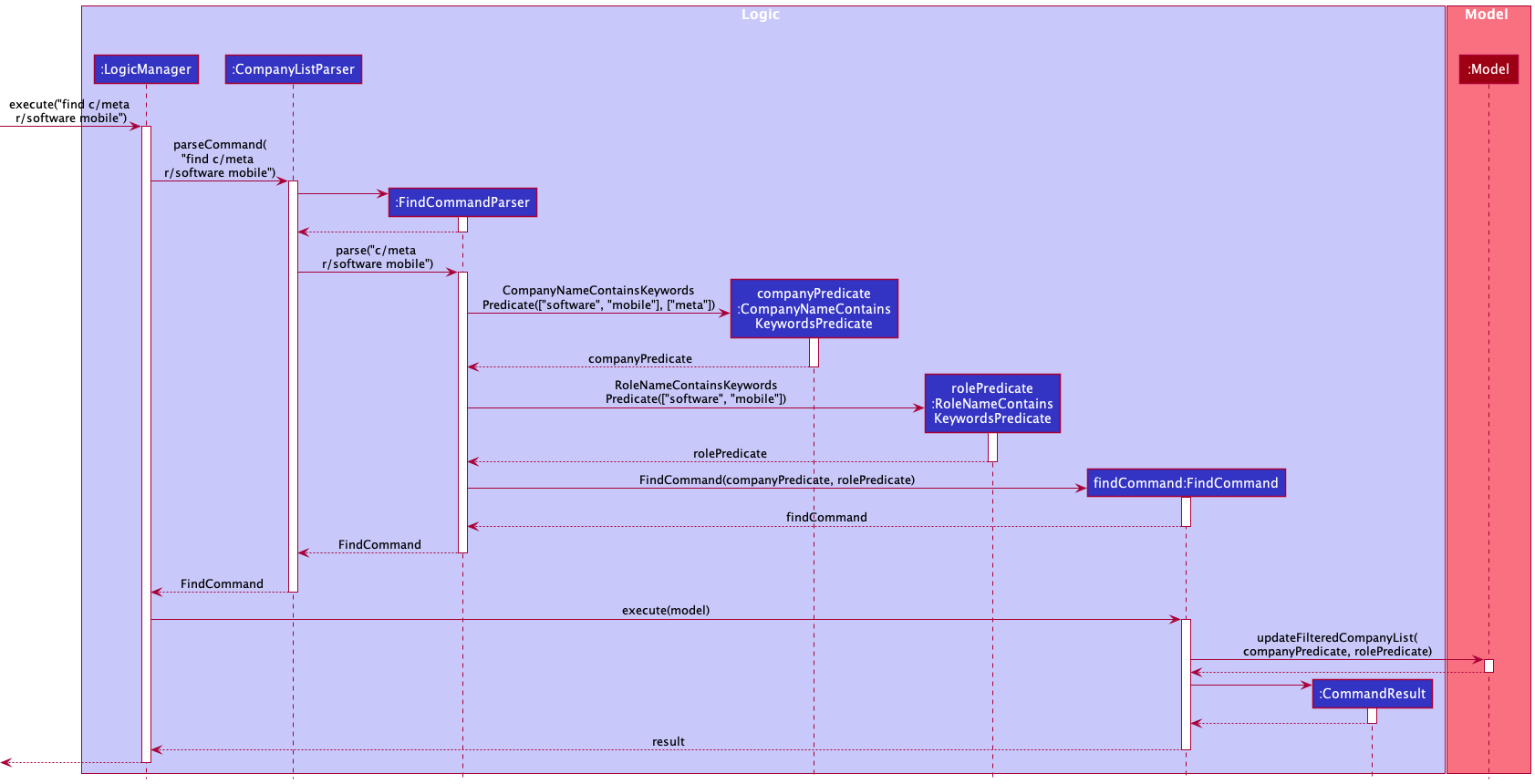
find c/meta r/software mobileto find roles whose role names contain role name keywordssoftwareormobile, which belong to companies whose company names contains the company name keywordmeta. - Then the
FindCommandParser#parse()creates aCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicateobject and aRoleNameContainsKeywordsPredicateobject with the role name keywords and company name keyword. - The
FindCommand#execute()method will update themodelusing theModel#updateFilteredCompanyList()method, displaying only roles that match the keywords, and the companies that they belong to. - The
Parserreturns theFindCommandtoLogicManagerwhich then returns theCommandResulttoMainWindowin order to display the changes to the user.
The following sequence diagram shows how the find command operation works with the user input find c/meta r/software mobile:
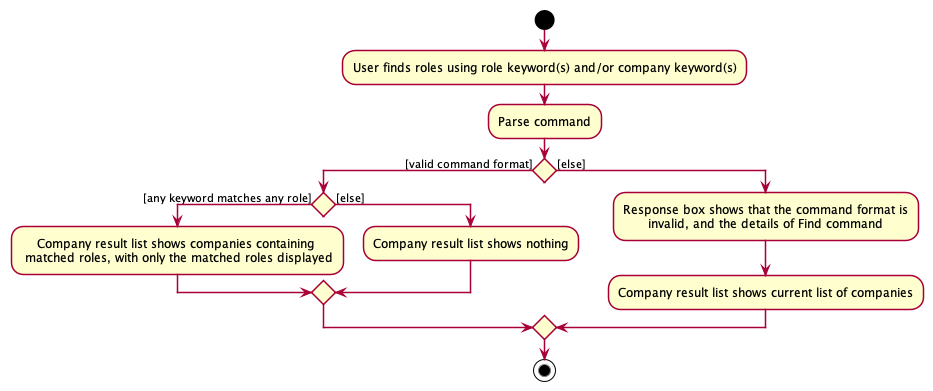
The following activity diagram summarises what happens when a user executes the find command:
Design considerations
- Alternative 1 (current choice): The use of one unified
findcommand with prefixesc/andr/to concurrently filter the company list by role name and company name.- Pros:
- Users are able to quickly sieve through the company list to find the specific roles.
- Cons:
- Increased dependencies and coupling between components, as
modelnow depends on both classesCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicateandRoleNameContainsKeywordsPredicate.
- Increased dependencies and coupling between components, as
- Pros:
- Alternative 2 (used in v1.2):
findonly allows users to filter the company list by company name keywords and not role name keywords.- Pros:
- Reduced coupling between components as
modeldepends onCompanyNameContainsKeywordsPredicatebut notRoleNameContainsKeywordsPredicate.
- Reduced coupling between components as
- Cons:
- Users have less flexibility in searching for specific roles, especially when they have applied for multiple roles within the same company. They can only find all roles which belong to specific companies.
- Pros:
Reminder feature
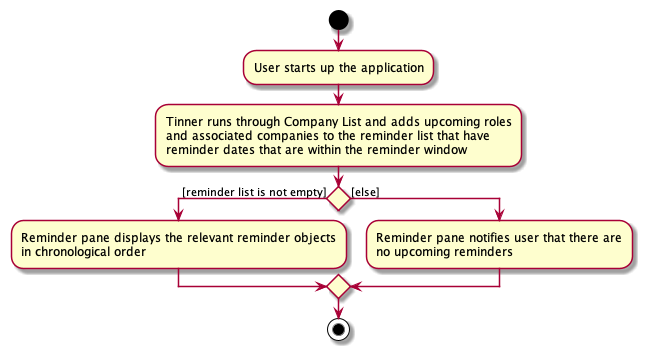
Whenever the user starts up the application, a reminder pane will automatically open along with the main window, showing all roles and their respective companies that have reminder dates that are within the reminder window.
The fields of the Reminder that will be shown are as follows:
CompanyNameRoleNameReminderDateStatus
Implementation
Given below is an example scenario on how the reminder feature works:
- The user has a role in a company with a reminder date of 30-04-2022 23:59.
- Assuming that the reminder window is at its default of 7 days, and today is within 7 days from 30th April 2022, when the user opens the application, the reminder pane will display the given role and its relevant fields as mentioned above.
The following sequence diagram shows how the reminder feature works:
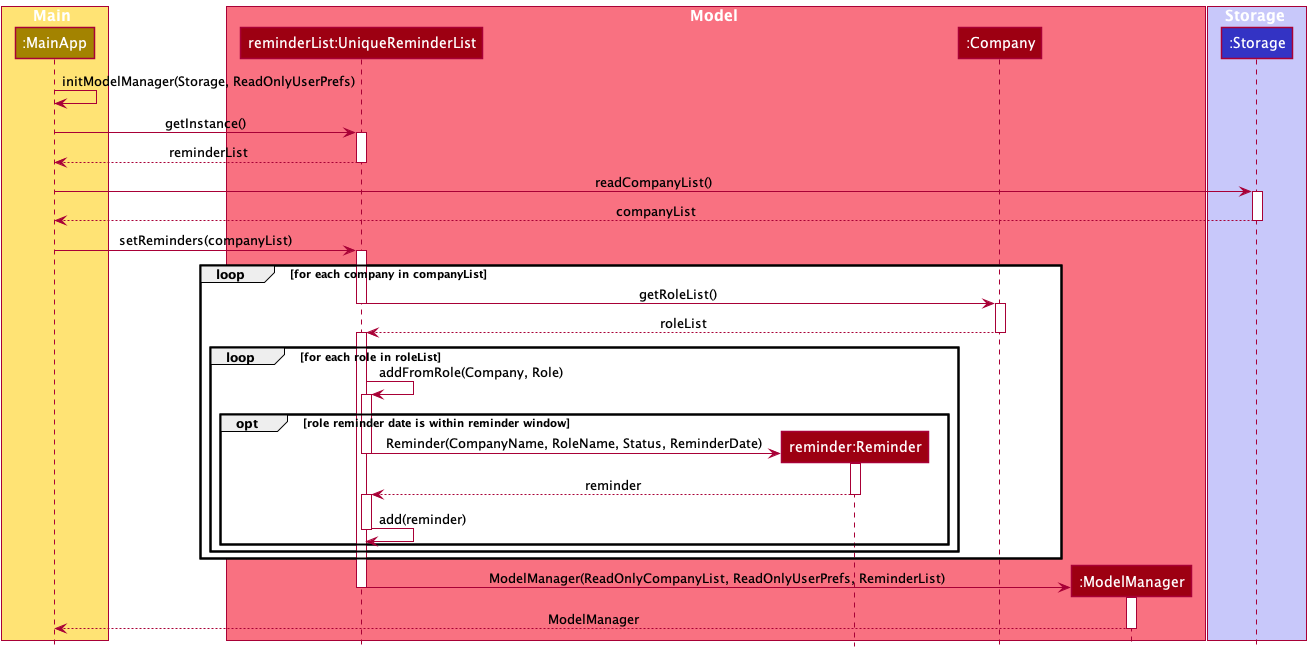
The following activity diagram summarises what happens when the user opens the application to see upcoming reminders:
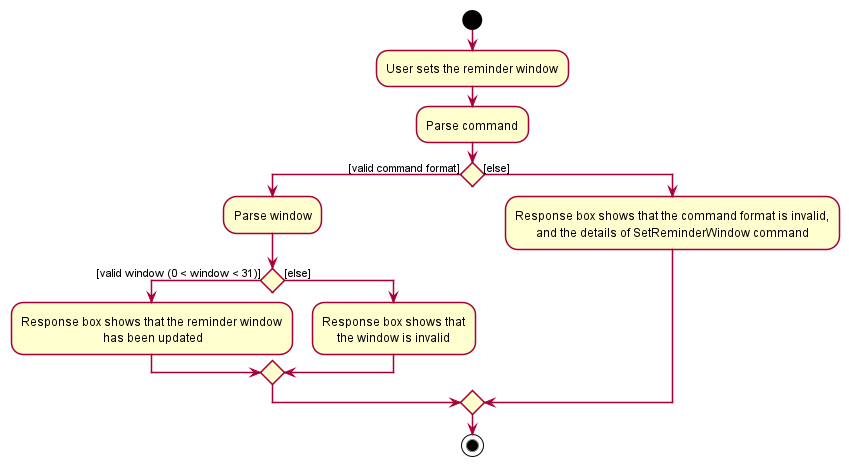
Set reminder window feature
The setWindow feature allows users to set the reminder window to a specific number of days. Any roles stored in the company list that fall within the set window will be displayed in the reminder pane that automatically opens up on start.
Implementation
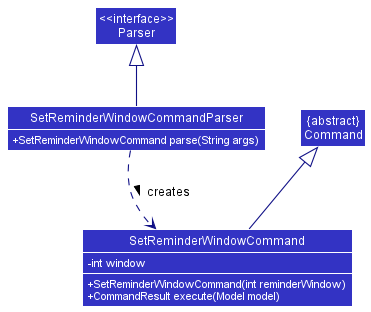
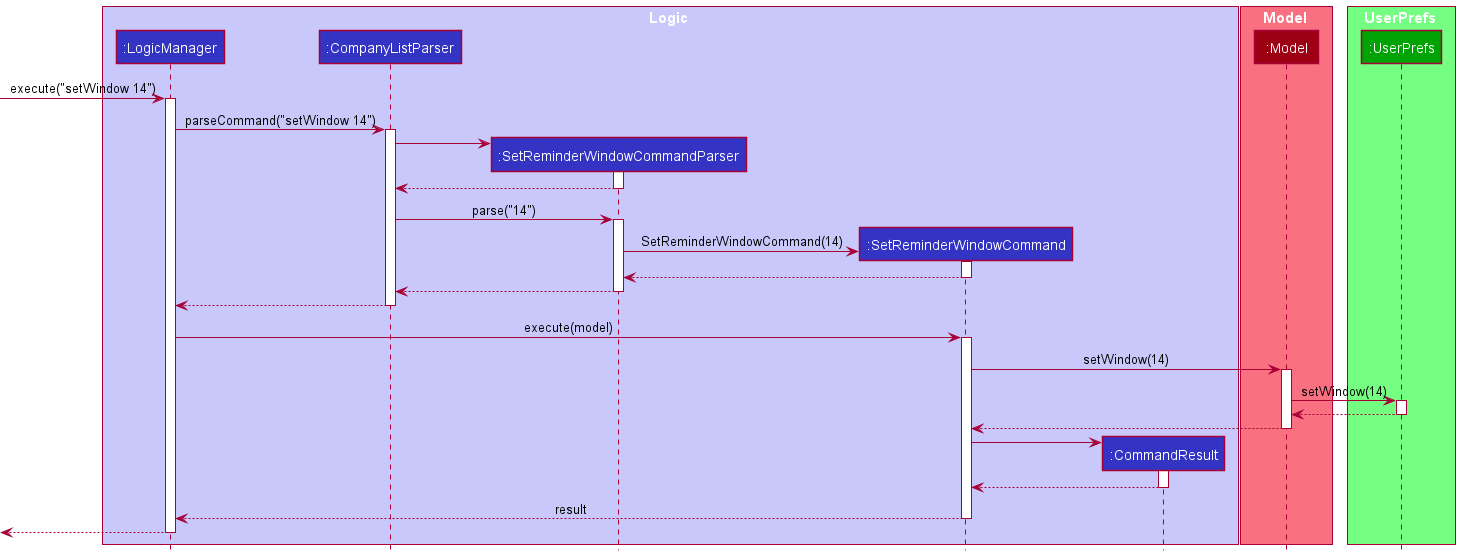
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the set reminder window feature behaves at each step:
- The user executes the command
setWindow 14to set the reminder window to 14 days. - Then the
SetReminderWindowCommandParser#parse()creates an instance ofSetReminderWindowCommandby passing the number of days to which the reminder window will be set. - The
SetReminderWindowCommand#execute()method will update themodelusing theModel#setReminderWindow()method, which consequently updatesuserPrefsby calling theUserPrefs#setReminderWindow()method to update the reminder window as stored in the user preferences. - The
Parserreturns theSetReminderWindowCommandtoLogicManagerwhich then returns theCommandResulttoMainWindowin order display the changes to the user.
The following sequence diagram shows how the setWindow command operation works with the user input setWindow 14:
The following activity diagram summarises what happens when a user executes the setWindow command:
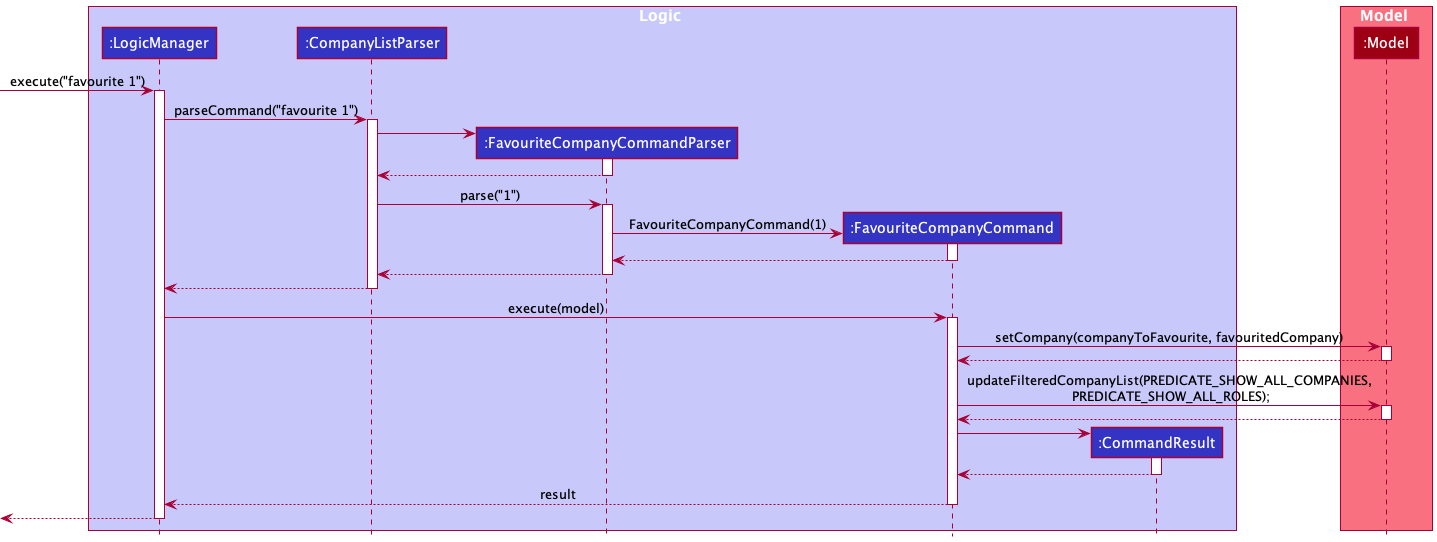
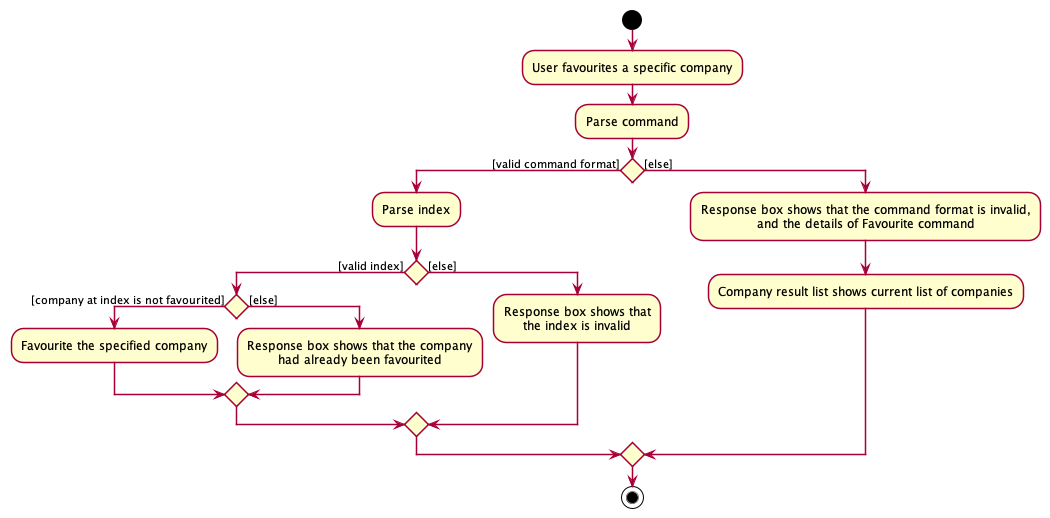
Favourite feature
The favourite feature allows users to highlight specific companies. Favourited companies are indicated using a star beside their company name in the GUI.
Implementation
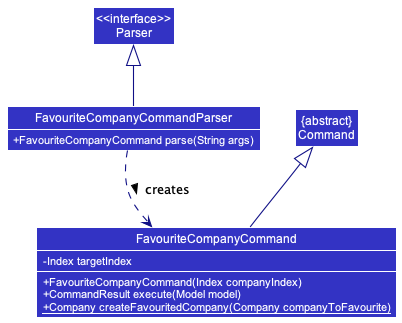
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the favourite feature behaves at each step:
- The user executes the command
favourite 1to favourite the first company within the displayed company list. - Then the
FavouriteCompanyCommandParser#parse()creates an instance ofFavouriteCompanyCommandby passing the company index to be favourited. - The
FavouriteCompanyCommand#execute()method will update themodelwith the favourited company using theModel#setCompany()method, replacing the previous company that was not favourited. - The
modelis then updated with theModel#updateFilteredCompanyList()method, displaying all companies and roles in the company list. - The
Parserreturns theFavouriteCompanyCommandtoLogicManagerwhich then returns theCommandResulttoMainWindowin order to display the changes to the user.
The following sequence diagram shows how the favourite command operation works with the user input favourite 1:
The following activity diagram summarises what happens when a user executes the favourite command:
Design considerations
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Although both
favouriteandeditCompanycommands edit fields within a specified company, we decided to make them two separate commands.- Pros:
- Users are able to favourite roles much more easily by just providing the index.
- More intuitive to users to use
favouriterather thaneditCompanyto favourite a company.
- Cons:
- This feature was more challenging to implement as compared to simply integrating the functionality of
favouriteintoeditCompany.
- This feature was more challenging to implement as compared to simply integrating the functionality of
- Pros:
- Alternative 2: Allowing the favourite status field of a company to be modified through
editCompany.- Pros:
- Users can modify all fields within a company, including the favourite status, with the use of one single command.
- Cons:
- It is less straightforward for users to use
editCompanyto favourite a company. This also means that the favourite status field will not stand out to users.
- It is less straightforward for users to use
- Pros:
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
Students who…
- want to keep track of tech internships
- are disorganised and tend to miss deadlines
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefer typing to mouse interactions
- are reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition:
- Tracks essential information such as statuses and deadlines at a glance.
- Reminds you of important deadlines so that you will not miss anything about your application.
- Allows you to Review the process and take down notes so that you can ace your next application.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
user | add a new company | add new internship roles to said company |
* * * |
user | add a new internship role | keep track of said internship application process |
* * * |
user | delete a company | remove companies that I am no longer interested in |
* * * |
user | delete an internship role | remove internship roles that are outdated or complete |
* * * |
user | see a summary of my internship applications at a glance | have a general overview of the status of my applications |
* * |
user | search keywords like company name, internship roles, etc. | locate my internship application quickly |
* * |
user | sort applications in chronological order of deadlines | keep track of the timeline of applications |
* * |
user | modify each item | keep Tinner and all its contents up to date |
* * |
user | be reminded of upcoming deadlines | be on time with my applications |
* * |
organised user | tag applications and events | keep items compartmentalised and thus easier to access |
* * |
new user | learn how to use the application via a guide | use the application periodically with ease |
* * |
user | mark certain entries as my favourites | view those that I am more interested in at a glance |
* |
user | sort company names in alphabetical order | locate a company that I may have forgotten about |
* |
user | export calendar dates of important events into a .ics or .pdf file | keep track of my events on an external platform |
* |
long term user | archive/hide irrelevant events | not get distracted by what is not important |
* |
user | export a list of interview reviews of different companies into a .csv file | share my experience with juniors and peers |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the Tinner and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC01 - Add a company
Guarantees: a company will be successfully created
MSS
- User requests to add a specific company and its information in the list
- Tinner adds a company to the list
-
Tinner displays the list of companies
Use case ends
Extensions
1a. The input does not adhere to the command format
1a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 1
1b. The specific company is already stored
1b1. Tinner shows a duplicate company error message
Use case resumes at step 1
Use case: UC02 - Edit a company
Precondition: there exists at least one company in Tinner
MSS
- User request to edit certain details of a specific company
- Tinner edits certain details specified by the user
-
Tinner displays the list of companies with updated details
Use case ends
Extensions
1a. The input does not adhere to the command format
1a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 1
1b. Company already exists in Tinner format
1b1. Tinner shows error that company is duplicated
Use case resumes at step 1
1c. Field restrictions violated
1c1. Tinner shows error that a specific restriction is violated
Use case resumes at step 1
Use case: UC03 - Delete a company
Precondition: there exists at least one company in Tinner
Guarantees: a company is successfully removed from Tinner
MSS
- User requests to view a list of companies
- Tinner shows a list of companies and the associated internship roles
- User requests to delete a specific company in the list
-
Tinner deletes the company
Use case ends
Extensions
3a. The input does not adhere to the command format
3a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3b. The input company index is invalid
3b1. Tinner shows a company index out of bounds error message
Use case resumes at step 2
Use case: UC04- Add an internship role
Precondition: the company to which the internship role will belong has already been created
Guarantees: an internship role will be successfully created
MSS
- User requests to view a list of companies
- User requests to add an internship role and provides the relevant details
-
Tinner adds the internship role to the list of roles of the specific company
Use case ends
Extensions
1a. The input does not adhere to the command format
1a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 1
Use case: UC05 - Edits an internship role
Precondition: there exists at least one role associated with a company in Tinner
MSS
- User requests to edit a specific internship role of a company
- Tinner edits certain details specified by the user
-
Tinner displays the list of companies with roles and its updated details
Use case ends
Extensions
1a. The input does not adhere to the command format
1a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 1
1b. The input company index is invalid
1b1. Tinner shows error that the company index is invalid message
Use case resumes at step 1
1c. The input internship role index is invalid
1c1. Tinner shows error that the role index is invalid message
Use case resumes at step 1
1d. Role already exists in Tinner format
1d1. Tinner shows error that role is duplicated
Use case resumes at step 1
1e. Field restrictions violated
1e1. Tinner shows error that a specific restriction is violated
Use case resumes at step 1
Use case: UC06 - Delete an internship role
Precondition: there exists at least one internship role associated with a company
Guarantees: a specified internship role is successfully removed from the associated company
MSS
- User requests to view a list of companies
- Tinner shows a list of companies and the associated internship roles
- User requests to delete a specific internship role of a company in the list
-
Tinner deletes the internship role
Use case ends
Extensions
3a. The input does not adhere to the command format
3a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3b. The input company index is invalid
3b1. Tinner shows a company index out of bounds error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3c. The input internship role index is invalid
3c1. Tinner shows an internship role index out of bounds error message
Use case resumes at step 2
Use case: UC07 - Find a company with an internship role
Precondition: there exists at least one internship role associated with a company
Guarantees: all internship role which matches the user input will be successfully displayed from all companies matches the user input
MSS
- User requests to find some internship roles in some company and provides keywords for both.
-
Tinner displays all companies that matches the company keyword and have at least one role which matches the role keyword.
Use case ends
Extensions
1a. The input does not adhere to the command format
1a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 1
1b. The input company keyword is invalid
1b1. Tinner shows invalid company name error message
Use case resumes at step 1
1c. The input role keyword is invalid
1c1. Tinner shows invalid role name error message
Use case resumes at step 1
1d. The input role keyword is absent
1d1. Tinner shows all companies that matches the company keyword and all their roles
Use case ends
1e. The input company keyword is absent
1e1. Tinner shows all companies with at least one role that matches the role keyword and display all
Use case ends
Use case: UC08 - List all companies
Precondition: there exist at least one company stored in Tinner
Guarantees: every company stored in Tinner will be shown
MSS
- User requests to view a list of companies
-
Tinner displays all companies in its storage
Use case ends
Use case: UC09 - Using the reminder feature
Precondition: there exist at least one company stored in Tinner
Guarantees: every role in companies that have reminder dates within the reminder window from today will be shown
MSS
- The user adds a role(UC02) or edits a role(UC05) that has a reminder date.
- Tinner shows success message and adds/edits the role.
- The user closes the application and opens it up again immediately or some time in the future
-
Tinner displays all roles in companies that have reminder dates within the reminder window from today’s date
Use case ends
Use case: UC10 - Using the set reminder window feature
Guarantees: the reminder window will be successfully updated
MSS
- User requests to update reminder window to a new reminder window
- Tinner updates the reminder window
-
The updated reminder window is reflected upon restarting the application
Use case ends
Extensions
1a. The input reminder window is invalid (i.e. negative or bigger than 30)
1a1. Tinner shows an invalid input reminder window error message
Use case resumes at step 1
Use case: UC11 - Favouriting a company and viewing all favourited companies
Precondition: there exist at least one company in Tinner
Guarantees: a company is successfully favourited within Tinner
MSS
- User requests to view a list of companies
- Tinner shows a list of companies and the associated internship roles
- User requests to favourite a specific company in the list
- Tinner favourites the company
- User requests to view all favourited companies
-
Tinner shows a list of all favourited companies and their associated internship roles
Use case ends
Extensions
3a. The input does not adhere to the command format
3a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3b. The input company index is invalid
3b1. Tinner shows a company index out of bounds error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3c. The specific company to be favourited had already been favourited
3c1. Tinner shows a company already favourited error message
Use case resumes at step 2
Use case: UC12 - Unfavouriting a company
Precondition: there exist at least one company in Tinner
Guarantees: a company is successfully unfavourited within Tinner
MSS
- User requests to view a list of companies
- Tinner shows a list of companies and the associated internship roles
- User requests to unfavourite a specific company in the list
-
Tinner unfavourites the company
Use case ends
Extensions
3a. The input does not adhere to the command format
3a1. Tinner shows an invalid input format error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3b. The input company index is invalid
3b1. Tinner shows a company index out of bounds error message
Use case resumes at step 2
3c. The specific company to be unfavourited is already unfavourited
3c1. Tinner shows a company already unfavourited error message
Use case resumes at step 2
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed - Should be able to hold up to 1000 items (companies and internship roles) without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage
- Should require no installation
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse
- Should be responsive and have a latency of less than 3 seconds
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, macOS
- CLI: Command Line Interface
- MSS: Main Success Scenario
- Command Box: Text field for users to key in their commands
-
Response Box: Tinner’s response to user’s commands.
If the command was successful, Tinner would respond with what it did. Else it tells you what went wrong and any tips to fix it
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Start and exit the application
- To start the application
- Download the tinner.jar file and copy into an empty folder.
- On the command terminal, run the following command in the directory containing tinner.jar:
java -jar tinner.jar
Expected: Shows the GUI with internship application examples.
- To exit the application
- Enter
exitin the command box.
Expected: The application will close shortly.
- Enter
Adding a company
- Test case:
addCompany n/Govtech p/9222222 e/xyz@gov.com a/10 Pasir Panjang Rd, #10-01 Mapletree Business City, Singapore 117438- Expected: Company list is updated with the addition of “GovTech”. The response box shows the details of all the fields added.
- Test case:
addCompany n/Tik Tok e/xyz@tiktok.com- Expected: Company list is updated with the addition of “Tik Tok”. The response box shows the details of the fields added.
- Test case:
addCompany e/t@tesla.com p/99944426 n/Tesla- Expected: Company list is updated with the addition of “Tesla”. The response box shows the details of the fields added.
- Test case:
addCompany n/Tinner p/ e/t@tinner.com a/fairy land- Expected: Company list is not updated. The response box shows error message that there must be a value after a prefix.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
addCompany, and other prefixes without value e.g.add n/.- Expected: Company list is not updated. The response box shows an error message that it is an invalid command with additional information of the correct command format.
Editing a company
- Prerequisites: At least 2 companies must exist and listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
editCompany 1 1 n/Tik Tok- Expected: The name of 1st company is changed to “TikTok”. The response box shows the updated details of all the fields of the edited company. The company list is updated with the changes.
- Test case:
editCompany 2 n/Tik Tok- Expected: The name 2nd company is not updated. The response box shows error message that the company already exists in the company list.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
editCompany,editCompany x n/VAlID_COMPANY_NAMEwhere x is an integer larger than the size of the company list or negative integer values.- Expected: The intended company with index
xis not updated. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company index provided is invalid.
- Expected: The intended company with index
Deleting a company
- Prerequisites: At least 2 companies must exist and listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
deleteCompany 1- Expected: First company with its roles included if any, is removed from the company list. The response box shows the details of the deleted company.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
deleteCompany,deleteCompany xwhere x is an integer larger than the size of the company list or negative integer values.- Expected: Company with index
xis not deleted. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company index provided is invalid.
- Expected: Company with index
Favouriting a company
- Prerequisites: At least 2 companies must exist with the first company in the company list already favourited (indicated with a star beside its name in the GUI), and listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
favourite 2- Expected: Second company in the displayed company list is favourited. The response box shows the details of the favourited company.
- Test case:
favourite 1- Expected: First company in the displayed company list is not favourited again as it is already favourited. The response box shows a message indicating that the company is already favourited.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
favourite,favourite xwhere x is an integer larger than the size of the company list or negative integer values.- Expected: Company with index
xis not favourited. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company index provided is invalid.
- Expected: Company with index
Unfavouriting a company
- Prerequisites: At least 2 companies must exist with the first company in the company list already favourited (indicated with a star beside its name in the GUI), and listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
unfavourite 1- Expected: First company in the displayed company list is unfavourited. The response box shows the details of the unfavourited company.
- Test case:
unfavourite 2- Expected: Second company in the displayed company list is not unfavourited as it is already unfavourited. The response box shows a message indicating that the company is already unfavourited.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
unfavourite,unfavourite xwhere x is an integer larger than the size of the company list or negative integer values.- Expected: Company with index
xis not favourited. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company index provided is invalid.
- Expected: Company with index
Adding a role
- Prerequisites: At least 1 companies must exist and listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
addRole 1 n/Frontend Engineer s/pending- Expected: The name of the lastest role from the 1st company is initialised as “Frontend Engineer”, with status of “pending”. The response box shows the details of all the fields of the newly added role. The company list is updated with the changes.
- Test case:
addRole 1 n/Frontend Engineer s/complete- Expected: No new role is added to the 1st company. The response box shows error message that the role already exists in the company.
- Test case:
addRole 1 s/complete $/1000- Expected: No new role is added to the 1st company. The response box shows error message that the format is wrong, this is due to required field (RoleName)) not being given.
- Test case:
addRole 1 n/Frontend Engineer s/complete $/- Expected: No new role is added to the 1st company. The response box shows error message that there must be a value after a prefix, regardless of if it is optional.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
addRole x1 n/VALID_ROLE_NAME s/VALID_STATUSwhere x1 is an integer larger than the size of the company list or negative integer values.- Expected: No new role is added to the 1st company. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company/role index provided is invalid.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
addRole x1 n/LONG_ROLE_NAME s/VALID_STATUS $/LONG_STIPENDwhere x1 is an integer larger than the size of the company list or negative integer values, and LONG_ROLE_NAME exceeds 30 characters, and LONG_STIPEND exceeds 14 characters.- Expected: No new role is added to the 1st company. The response box shows error message that the role name character limit is 30 characters/the stipend character limit is 14 characters.
Editing a role
- Prerequisites: At least 1 company with 2 roles must exist and is listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
editRole 1 1 n/Frontend Engineer- Expected: The name of 1st role from the 1st company is changed to “Frontend Engineer”. The response box shows the updated details of all the fields of the edited role. The company list is updated with the changes.
- Test case:
editRole 1 2 n/Frontend Engineer- Expected: The name of 2nd role from the 1st company is not updated. The response box shows error message that the role already exists in the company.
- Test case:
editRole 1 1 $/0- Expected: The stipend of 1st role from the 1st company is not updated. The response box shows error message that stipend must be a positive number.
- Test case:
editRole 1 1 $/10000000000oreditRole 1 1 $/0- Expected: The stipend of 1st role from the 1st company is not updated. The response box shows error message that stipend must be a positive value and input of stipend should be at most 10 digits long.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
editRole,editRole x1 x2 n/VAlID_ROLE_NAMEwhere x1 or x2 are integers larger than the size of the company list and role list respectively or negative integer values.- Expected: The intended company with index
x1and role with indexx2is not updated. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company/role index provided is invalid.
- Expected: The intended company with index
Deleting a role
- Prerequisites: At least 1 companies with 2 roles must exist and listed using the
listcommand - Test case:
deleteRole 1 1- Expected: The name of 1st role from the 1st company is deleted. The response box shows the details of all the fields of the deleted role. The company list is updated with the changes.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
deleteRole,deleteRole x1 x2where x1 or x2 are integers larger than the size of the company list and role list respectively or negative integer values.- Expected: The intended role at company with index
x1and role with indexx2is not deleted. The response box shows error message that it is an invalid command or company/role index provided is invalid.
- Expected: The intended role at company with index
Finding a role
- Prerequisites: There must be 2 companies which are listed using the
listcommand. The first company must have the namemetacontaining a role with the namesoftware engineerfollowed by another role with the namedata engineer. The second company must have the namegooglecontaining a role with the namemobile engineerfollowed by another role with the namedata engineer. - Test case:
find c/meta- Expected: Only the first company is displayed with both its roles.
- Test case:
find r/engineer- Expected: Both companies are displayed with all their roles.
- Test case:
find c/google r/data- Expected: Only the second company is displayed with only its
data engineerrole shown.
- Expected: Only the second company is displayed with only its
- Test case:
find r/data- Expected: Both companies are displayed with only their respective
data engineerroles shown.
- Expected: Both companies are displayed with only their respective
- Test case:
find c/meta r/engineer- Expected: Only the first company is displayed with both its roles.
- Test case:
find c/meta r/mobile- Expected: No companies are displayed.
- Test case:
find r/mobile data software- Expected: Both companies are displayed with all their roles.
- Test case:
find c/,find r/,find c/ r/- Expected: The response box shows an error message that it is an invalid command as there must be a value after prefix.
- Other incorrect test cases to try:
find,find test,find a/ b/- Expected: The response box shows an error message that it is an invalid command with additional information of the correct command format.
Using the reminder feature
- Prerequisites: At least 1 company with one role must exist and is listed on index 1 using the
listcommand, test cases assume default reminder window of 7 days is used - Test case:
editRole 1 n/Software Engineer r/<INSERT DATE THAT IS WITHIN 7 DAYS FROM TODAY>(e.g. if today is 06-04-2022, test case should use any date between 06-04-2022 to 13-04-2022)- Expected: When you close and reopen the application, the reminder pane will show the added role.
- Test case:
editRole 1 n/Software Engineer r/<INSERT DATE THAT IS IN THE PAST>(e.g. if today is 06-04-2022 , use any date before then like 05-04-2022)- Expected: The response box shows an error message that the reminder date should not be in the past.
- Test case:
editRole 1 n/Software Engineer r/<INSERT INVALID DATE>(e.g. 31-04-2022)- Expected: THe response box shows an error message that the reminder date should be a valid date.
Appendix: Effort
Tinner is a challenging venture as we are modifying the AB3 address book application to an internship application. The introduction of Role requires much consideration into the interaction, management and storage of information within and across components to ensure ample usage of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and Design Patterns. Moreover, there were many modifications to AB3’s commands, such as find to optimise searches on internship applications within Tinner. As a result, there were major changes in components such as Model and Logic while seeking out the best design practices. Additionally, the Reminder feature requires a separate window thus, designing a new interface is required to display essential information.
Some of the difficulties and challenges faced when implementing the features are as followed:
-
addRole,editRole,deleteRole: Even though the implementation ofRolecommands are adapted from the commands in AB3, it was challenging due to the close coupling betweenCompanyandRole. While having separate logic and commands for both entities, there is also a need to ensure data consistency for cases such asRolecannot exist withoutCompany. Thus, features such asdeleteCompanyhave a cascade effect where the removing of a company will remove allRoleassociated with it.
-
find: The implementation of the find was different from that of AB3’s as we needed to account for two separate search predicates: company and role. Thus, it was rather complicated due to the fact that we had to run the company list through multiple filters based on different search scenarios such as when just the role is specified, just the company is specified, or both.
-
reminder: The implementation of the reminder system was rather tricky because it was our first time using the singleton pattern across the application. The UniqueReminderList behaves as a class that contains a single instance of a reminder list that can be retrieved with getInstance(); this took a while to get used to as it meant that the reminder list could be readily retrieved from almost anywhere within the application. The second hurdle was the implementation of the actual reminder window, since it involved the creation of new UI components and entailed several changes to the UniqueReminderList in terms of how Reminder items were retrieved. Wireframing software like Figma especially came in handy when drafting out the UI components before the writing them in JavaFX.
-
setWindow: The implementation of the setWindow command is quite unique as it is the only command that edits the UserPrefs. Challenges faced with this implementation included the testing of the command as the update of the reminder window only occurs after the application is restarted, making it only possible to test manually.
Overall, we estimate our effort to be 20% more than the implementation of AB3. This is due to the implementation of Role as a key entity with many closely coupled relationships with other components. Also, managing both Role and Company entities separately, and we implemented close to double the key features implemented in AB3.